Benzalkonium Chloride is a well-known antiseptic with a long history of use in a wide range of human and veterinary products. It acts on a wide range of microorganisms, from gram+ to gram- bacteria, moulds and yeasts.
Our FeF Benzalkonium Chloride is odourless and colourless, and its effectiveness in all pH ranges, combined with its ability to mix well in most formulations, makes it an ideal antimicrobial ingredient.
Applications
No matter the application, formulations that come into contact with either healthy or damaged buccal tissue must utilize only the purest and safest ingredients.
FeF Benzalkonium Chloride can be used either as excipients or active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) for oral and dental formulations.
Lozenges: FeF Benzalkonium Chloride (BKC) is used as an API in lozenges to treat superficial infections in the mouth and throat.
Gels and creams: FeF Benzalkonium Chloride (BKC) is also often found in gels and creams at typical concentrations of 0,01 to 0,1%, to treat herpes and cold sores infections or as an excipient in pain-relieving gum gels.
Antiseptic mouth sprays with FeF Benzalkonium Chloride (BKC) are also common. Dentistry products: FeF Benzalkonium Chloride is also used either as an active antiseptic or a preservative in, for example, rinsing fluids and antiseptic fills.
Antimicrobial effect
FeF Benzalkonium Chloride is effective at all pH levels. However its effectiveness increases when the pH increases. The higher the pH, the lower the concentration needed to obtain an antimicrobial effect.
As opposed to bacteriostatic/fungistatic compounds which only prevent micro-organisms from dividing (growing), Benzalkonium Chloride is bactericidal/fungicidal, meaning they will kill micro-organisms, whether they are in a growth phase or not.
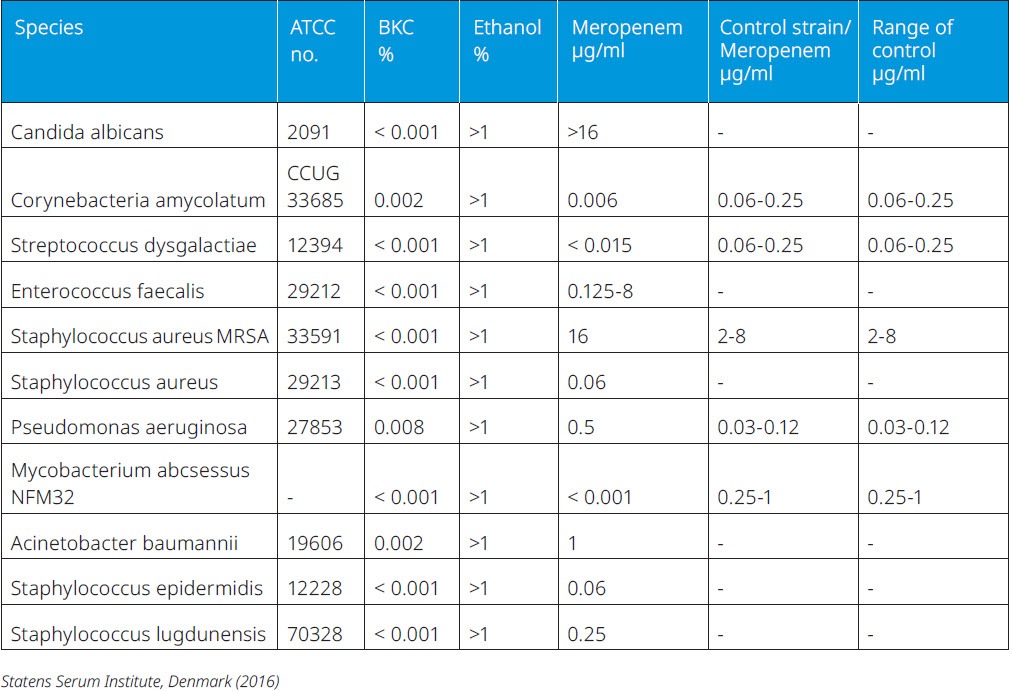
FeF Benzalkonium Chloride has been tested against several relevant microbial strains, and shown to be effective against a wide range of micro-organisms at low concentrations. FeF Benzalkonium Chloride is compared here with ethanol and with a positive control containing Meropenem (a broad-spectrum antibiotic).
Table 1: Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations. Mean results in % or μg/ml.